Common Bookkeeping Mistakes to Avoid A Guide
Common bookkeeping mistakes to avoid can significantly impact a business’s financial health. This guide delves into the most frequent errors, from recording transactions to categorizing them and applying accounting principles. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for accurate financial reporting and avoiding potential legal issues.
This comprehensive resource examines the top five bookkeeping errors related to recording transactions, offering detailed explanations and real-world examples. We’ll also explore the importance of proper categorization, discuss the implications of ignoring accounting principles, and provide practical steps to prevent these errors in your business. The guide includes tables and step-by-step procedures to help you master correct bookkeeping practices.
Common Errors in Recording Transactions

Source: com.au
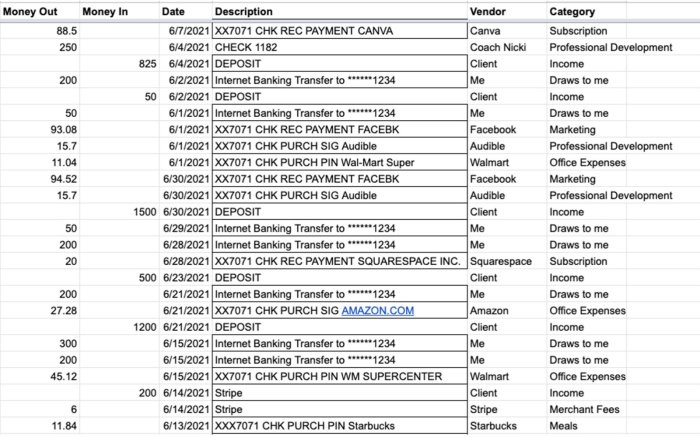
Accurately recording transactions is fundamental to sound bookkeeping. Inaccurate entries can lead to significant financial reporting discrepancies, impacting profitability analysis and decision-making. Understanding and mitigating these errors is crucial for maintaining financial integrity and fostering trust with stakeholders.
Top 5 Frequent Bookkeeping Errors in Transaction Recording
A thorough understanding of common bookkeeping errors is essential for preventing them. These errors, if not identified and corrected, can distort financial reports and negatively affect a business’s financial health.
- Incorrect Account Classification: Miscategorizing transactions into the wrong accounts is a prevalent error. This occurs when a business owner or bookkeeper fails to match the transaction’s nature with the appropriate account (e.g., recording a rent expense as a utility expense). The impact on financial statements is a misrepresentation of expenses or revenues, leading to inaccurate profit margins and potentially impacting tax obligations.
- Omitting Supporting Documentation: Failing to maintain adequate documentation for transactions, such as receipts, invoices, or contracts, can hinder accurate recording. This often results in inconsistencies and makes reconciliation challenging. The consequences include difficulty in verifying the accuracy of entries and potential for fraud. This error impacts financial statements by leading to missing information and making the financial statements incomplete.
- Incorrect Date Recording: Recording transactions on the wrong date, either earlier or later than the actual transaction date, can significantly distort financial reports. This error impacts the accuracy of the income statement and balance sheet, leading to timing discrepancies. For example, recording a sale in the wrong month might inflate or deflate sales figures for that period.
- Incorrect Amount Recording: Transcribing incorrect amounts from source documents to the accounting system is another common error. This often occurs due to manual data entry or using inaccurate information from supporting documents. This error distorts the financial statements, as revenues or expenses are not recorded correctly, affecting the overall financial picture.
- Lack of Proper Reconciliation: Failing to reconcile bank statements with accounting records regularly can result in unrecorded transactions or discrepancies in cash balances. This can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and may even obscure fraudulent activities. The impact on financial statements is an inaccurate representation of the cash balance, which affects the balance sheet and cash flow statement.
Examples of Incorrectly Recorded Transactions
Illustrative examples of common errors and the correct recording methods are presented below:
| Transaction Type | Incorrect Recording | Correct Recording | Impact on Financial Statements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase of Supplies | Recorded as Rent Expense | Recorded under Supplies Expense account | Incorrect expense classification; inaccurate profit calculation |
| Payment of Salaries | Recorded on the wrong date | Recorded on the actual payment date | Incorrect timing of expenses; distorts income statement; potential tax implications |
| Sale of Goods | Recorded with an incorrect amount | Recorded with the exact amount from the invoice | Inaccurate revenue; misrepresentation of sales figures; possible tax discrepancies |
| Receipt of Payment | Not recorded | Recorded as cash receipt | Understatement of cash balance; incomplete cash flow statement |
| Utilities Expense | Recorded under the wrong month | Recorded under the correct month | Incorrect expenses for the period; misrepresentation of expenses for the period |
Step-by-Step Procedure to Prevent Common Errors in Recording Cash Transactions
To minimize errors in recording cash transactions, follow these steps:
- Thorough Documentation: Always obtain and retain copies of all supporting documents, including receipts, invoices, and bank statements.
- Accurate Data Entry: Carefully review and double-check all data before entering it into the accounting system.
- Regular Reconciliation: Reconcile bank statements with accounting records regularly to identify any discrepancies.
- Internal Controls: Implement strong internal controls, including separation of duties and authorization procedures.
- Proper Training: Ensure all staff involved in recording cash transactions are properly trained on accounting procedures.
Issues with Categorization and Classification
Accurate categorization and classification of transactions are fundamental to sound bookkeeping practices. Inaccurate categorization can lead to significant distortions in financial reports, hindering informed decision-making and potentially impacting tax obligations. This section will delve into common errors in this crucial area, highlighting the importance of correct categorization and offering practical examples for improved accuracy.
Misclassifying transactions can obscure the true financial picture, leading to inaccurate profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. This, in turn, can impact a business’s ability to make sound financial decisions, understand its performance, and manage its finances effectively. Correct categorization is essential to maintain financial transparency and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Common Mistakes in Categorization
Categorization errors often arise from a lack of clear guidelines or inconsistencies in applying established procedures. Insufficient training, inadequate documentation, or simply human error can contribute to these mistakes. Using broad categories or relying on memory instead of documented procedures can lead to inaccuracies. Failure to consistently apply the same criteria to similar transactions across periods can also result in inconsistent reporting.
Importance of Accurate Categorization in Financial Reporting
Accurate categorization is crucial for several reasons. It ensures that expenses are correctly allocated to specific departments or activities, allowing for a precise understanding of operational costs. It facilitates precise tracking of revenue sources, providing insights into the profitability of different product lines or services. Accurate classification also ensures compliance with accounting standards and tax regulations, avoiding potential penalties.
Illustrative Examples of Incorrect Categorization
| Transaction Description | Incorrect Category | Correct Category |
|---|---|---|
| Payment for office supplies | General Expenses | Office Supplies |
| Payment for advertising campaign | Salaries | Marketing Expenses |
| Payment for consulting services | Administrative Expenses | Professional Services |
| Sales revenue from online orders | General Income | Online Sales |
Different Categorization Methods and Their Pros/Cons
Different methods for categorizing transactions exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common methods include using predefined categories, implementing automated systems, or relying on manual procedures.
- Predefined Categories: Using a pre-defined chart of accounts is a common method. Pros include consistency and standardization. Cons can arise if the categories are too broad or don’t accommodate specific business needs.
- Automated Systems: Software solutions often provide automated categorization based on pre-set rules. Pros include speed and reduced manual errors. Cons include the potential for incorrect categorization if the rules are not properly configured.
- Manual Procedures: Manual categorization requires careful judgment and consistency. Pros include flexibility to accommodate specific business needs. Cons include the higher risk of human error and the potential for inconsistencies if not properly documented.
Resources for Learning Best Practices
Numerous resources can assist in learning best practices for transaction classification. Professional accounting bodies, such as the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), offer guidance on accounting standards and best practices. Online courses, workshops, and seminars can provide in-depth knowledge and practical applications. Experienced bookkeepers or accountants can provide valuable insights and mentorship.
Ignoring or Misapplying Accounting Principles

Source: com.sg
Ignoring or misapplying generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) can have serious consequences for a business. Inaccurate financial reporting can lead to misguided decision-making, impacting profitability, investor confidence, and even legal repercussions. This section will detail how adhering to GAAP safeguards a company’s financial integrity and reputation.
Misapplication of accounting principles can lead to a distorted view of a company’s financial health. For instance, improperly valuing assets or failing to account for liabilities can inflate profits in the short term, masking underlying financial problems. This deceptive practice can result in misleading investors and creditors, ultimately harming the company’s long-term viability. Further, these inaccuracies can lead to regulatory scrutiny and potential legal challenges.
Accrual Accounting Mistakes
Accrual accounting, a method that records revenue when earned and expenses when incurred, is crucial for accurate financial reporting. Common mistakes include failing to record revenue from services performed but not yet billed, or recognizing expenses before they are actually incurred. These omissions can significantly skew a company’s profitability, leading to an inaccurate picture of its financial performance.
Deferral Accounting Mistakes
Deferral accounting, where revenue or expenses are recognized at a later date, also presents potential pitfalls. Misapplication often stems from failing to recognize the timing difference between cash inflows/outflows and the actual recognition of revenue/expenses. For example, prepaying rent for an upcoming period should not be recognized as an expense immediately; it should be deferred and recognized over the period it covers.
Matching Principle Application
The matching principle mandates that expenses be recognized in the same period as the revenues they generate. Correctly applying this principle ensures that the financial statements accurately reflect the costs associated with earning revenue during a specific period. Failure to do so leads to an overstatement or understatement of profits. A crucial aspect of this principle involves aligning costs with the revenue they directly support. For example, if a company spends money on advertising in January to generate sales in February, the advertising expense should be recorded in January, even if the payment is made in February.
Revenue Recognition Principle Application, Common bookkeeping mistakes to avoid
The revenue recognition principle dictates that revenue should be recognized when it’s earned, regardless of when cash is received. This principle requires careful consideration of the specific business transaction. Common mistakes include recognizing revenue before it’s earned or failing to recognize revenue earned but not yet collected. Correct application of this principle ensures a clear understanding of the company’s earnings capacity. For example, if a company provides a service on credit in January, but receives payment in February, the revenue should be recognized in January, not February.
Examples of Principle Application
| Business Scenario | Matching Principle Application | Revenue Recognition Principle Application |
|---|---|---|
| Software company selling a license | Software development costs should be matched with the revenue generated from the license sale. | Revenue is recognized when the license is sold, not when the payment is received. |
| Construction company | Costs of materials and labor directly related to a construction project should be matched with the revenue recognized from that project. | Revenue is recognized as the construction project progresses, based on the percentage of completion. |
| Subscription service | Recurring costs of maintaining the service should be matched with the revenue generated from the subscription. | Revenue is recognized monthly or annually based on the subscription period, not when the entire payment is received. |
Final Thoughts: Common Bookkeeping Mistakes To Avoid
In conclusion, meticulous bookkeeping is essential for any successful business. By understanding and avoiding common errors in recording transactions, categorization, and application of accounting principles, businesses can maintain accurate financial records, enhance transparency, and make informed decisions. This guide provides a practical framework for implementing best practices, empowering you to navigate the complexities of bookkeeping with confidence.